What if your content management system could think?
Not in a science-fiction, take-over-the-world kind of way. But in a practical, “here’s a better meta description for this article” way. In a “these taxonomy tags would improve your SEO” way. In a “your introduction could be more engaging” way.
That future is now. And in this tutorial, I’m going to show you exactly how to build it.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a fully functional AI Content Assistant integrated into Drupal 11.3 that will transform how your editorial team creates content. We’re talking real code, working examples, and production-ready architecture.
Let’s build something legendary.
Why Should You Care About AI in Your CMS?
Before we dive into code, let’s talk about why this matters.
The content creation bottleneck is real. According to Content Marketing Institute’s 2025 report, 67% of marketing teams cite “creating enough quality content” as their biggest challenge. Your editors are spending hours on repetitive tasks:
| Task | Average Time | AI-Assisted Time | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Writing meta descriptions | 15 min | 30 sec | 97% |
| Tagging content | 10 min | 5 sec | 99% |
| SEO optimization review | 30 min | 2 min | 93% |
| Content outline creation | 45 min | 5 min | 89% |
That’s not just efficiency—it’s hours per article returned to your team for actual creative work.
But here’s what makes Drupal 11.3 special: it was designed with AI integration in mind. The new AI API module, introduced in core contrib, provides standardized interfaces for connecting to any Large Language Model (LLM) provider. This means your AI assistant isn’t locked into OpenAI—you can swap providers, use local models, or even hybrid approaches.
The Architecture: How It All Fits Together
Before we write a single line of code, let’s understand what we’re building.
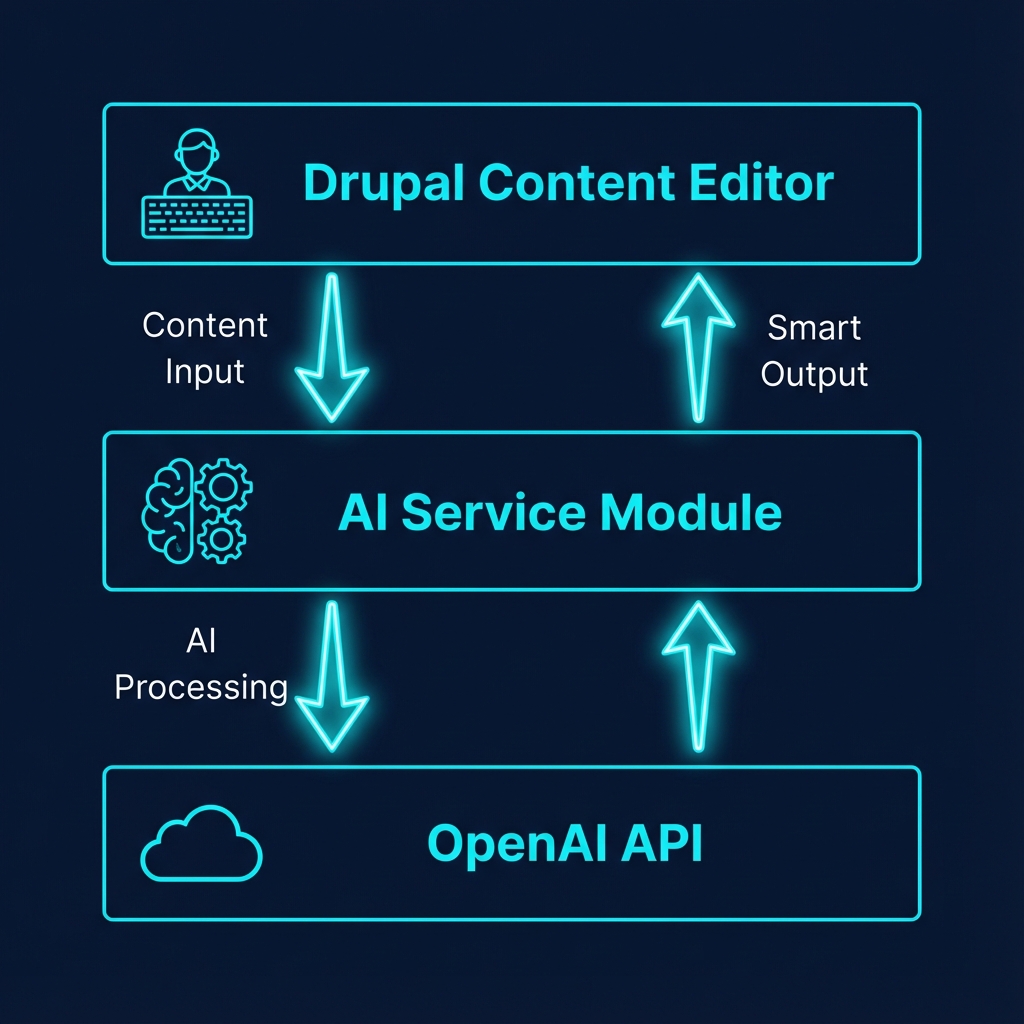
Our AI Content Assistant has three main components:
1. The Content Editor Interface
This is what your editors see. We’ll add AI-powered buttons directly in the node edit form that trigger suggestions for:
- Meta descriptions (auto-generated from body content)
- Taxonomy tags (intelligent suggestions based on content analysis)
- Content improvements (readability, SEO, engagement tips)
2. The AI Service Layer
A custom Drupal service that handles:
- Connection management to the AI provider
- Prompt engineering (this is where the magic happens)
- Response parsing and validation
- Caching for performance
3. The LLM Provider
We’ll use OpenAI’s GPT-4 for this tutorial, but the architecture supports:
- Anthropic Claude
- Google Gemini
- Local models via Ollama
- Azure OpenAI for enterprise compliance
Prerequisites: What You Need
Before we begin, ensure you have:
| Requirement | Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Drupal | 11.3+ | Core installation with Composer |
| PHP | 8.2+ | With curl extension enabled |
| OpenAI API Key | - | Get one at platform.openai.com |
| Composer | 2.x | For dependency management |
| Node.js | 20+ | For building JavaScript components |
Got all that? Let’s build.
Step 1: Create the Custom Module Structure
First, let’s scaffold our module. I like to call it ai_content_assistant:
mkdir -p web/modules/custom/ai_content_assistant
cd web/modules/custom/ai_content_assistantCreate the module info file:
# ai_content_assistant.info.yml
name: 'AI Content Assistant'
type: module
description: 'AI-powered content creation assistance for editors'
core_version_requirement: ^11
package: Custom
dependencies:
- drupal:node
- drupal:taxonomy
- drupal:field
configure: ai_content_assistant.settingsNow the services file—this is where we define our AI service:
# ai_content_assistant.services.yml
services:
ai_content_assistant.ai_service:
class: Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service\AIService
arguments:
- '@config.factory'
- '@http_client'
- '@cache.default'
- '@logger.factory'
ai_content_assistant.prompt_builder:
class: Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service\PromptBuilder
arguments:
- '@entity_type.manager'Step 2: Build the AI Service
This is the heart of our assistant. Create src/Service/AIService.php:
<?php
namespace Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service;
use Drupal\Core\Config\ConfigFactoryInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Cache\CacheBackendInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Logger\LoggerChannelFactoryInterface;
use GuzzleHttp\ClientInterface;
use GuzzleHttp\Exception\GuzzleException;
/**
* Service for AI-powered content assistance.
*/
class AIService {
/**
* The OpenAI API endpoint.
*/
protected const API_ENDPOINT = 'https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions';
/**
* Constructs the AI Service.
*/
public function __construct(
protected ConfigFactoryInterface $configFactory,
protected ClientInterface $httpClient,
protected CacheBackendInterface $cache,
protected LoggerChannelFactoryInterface $loggerFactory,
) {}
/**
* Generate a meta description for the given content.
*
* @param string $title
* The content title.
* @param string $body
* The content body text.
*
* @return string
* AI-generated meta description.
*/
public function generateMetaDescription(string $title, string $body): string {
$prompt = $this->buildMetaDescriptionPrompt($title, $body);
return $this->callOpenAI($prompt, [
'max_tokens' => 160,
'temperature' => 0.7,
]);
}
/**
* Suggest taxonomy tags for the given content.
*
* @param string $content
* The full content text.
* @param array $existingTags
* Array of existing tag names in the vocabulary.
*
* @return array
* Array of suggested tag names.
*/
public function suggestTags(string $content, array $existingTags): array {
$prompt = $this->buildTagSuggestionPrompt($content, $existingTags);
$response = $this->callOpenAI($prompt, [
'max_tokens' => 200,
'temperature' => 0.5,
]);
// Parse comma-separated response into array
$tags = array_map('trim', explode(',', $response));
return array_filter($tags);
}
/**
* Analyze content and provide improvement suggestions.
*
* @param string $title
* The content title.
* @param string $body
* The content body.
*
* @return array
* Array with 'score' and 'suggestions' keys.
*/
public function analyzeContent(string $title, string $body): array {
$prompt = $this->buildAnalysisPrompt($title, $body);
$response = $this->callOpenAI($prompt, [
'max_tokens' => 500,
'temperature' => 0.3,
]);
return $this->parseAnalysisResponse($response);
}
/**
* Call the OpenAI API.
*
* @param string $prompt
* The prompt to send.
* @param array $options
* Additional options (max_tokens, temperature).
*
* @return string
* The AI response.
*/
protected function callOpenAI(string $prompt, array $options = []): string {
$config = $this->configFactory->get('ai_content_assistant.settings');
$apiKey = $config->get('openai_api_key');
if (empty($apiKey)) {
throw new \RuntimeException('OpenAI API key not configured.');
}
// Check cache first
$cacheId = 'ai_response:' . md5($prompt);
if ($cached = $this->cache->get($cacheId)) {
return $cached->data;
}
try {
$response = $this->httpClient->request('POST', self::API_ENDPOINT, [
'headers' => [
'Authorization' => 'Bearer ' . $apiKey,
'Content-Type' => 'application/json',
],
'json' => [
'model' => $config->get('model') ?? 'gpt-4-turbo-preview',
'messages' => [
[
'role' => 'system',
'content' => 'You are a helpful content assistant for a professional website. Be concise and direct.',
],
[
'role' => 'user',
'content' => $prompt,
],
],
'max_tokens' => $options['max_tokens'] ?? 300,
'temperature' => $options['temperature'] ?? 0.7,
],
]);
$data = json_decode($response->getBody()->getContents(), TRUE);
$result = $data['choices'][0]['message']['content'] ?? '';
// Cache for 1 hour
$this->cache->set($cacheId, $result, time() + 3600);
return trim($result);
}
catch (GuzzleException $e) {
$this->loggerFactory->get('ai_content_assistant')
->error('OpenAI API error: @message', ['@message' => $e->getMessage()]);
throw new \RuntimeException('AI service temporarily unavailable.');
}
}
/**
* Build the meta description prompt.
*/
protected function buildMetaDescriptionPrompt(string $title, string $body): string {
// Truncate body to avoid token limits
$truncatedBody = substr(strip_tags($body), 0, 2000);
return <<<PROMPT
Generate an SEO-optimized meta description for this article.
Title: {$title}
Content excerpt:
{$truncatedBody}
Requirements:
- Maximum 155 characters
- Include the main keyword naturally
- Create urgency or curiosity
- Make it actionable
Return ONLY the meta description, nothing else.
PROMPT;
}
/**
* Build the tag suggestion prompt.
*/
protected function buildTagSuggestionPrompt(string $content, array $existingTags): string {
$tagList = implode(', ', array_slice($existingTags, 0, 50));
$truncatedContent = substr(strip_tags($content), 0, 1500);
return <<<PROMPT
Analyze this content and suggest relevant taxonomy tags.
Content:
{$truncatedContent}
Existing tags in the system (prefer these when relevant):
{$tagList}
Requirements:
- Suggest 3-5 tags maximum
- Prefer existing tags when they fit
- Create new tags only if essential
- Focus on topics, not generic terms
Return ONLY a comma-separated list of tags, nothing else.
PROMPT;
}
/**
* Build the content analysis prompt.
*/
protected function buildAnalysisPrompt(string $title, string $body): string {
$truncatedBody = substr(strip_tags($body), 0, 2500);
return <<<PROMPT
Analyze this article for quality and SEO.
Title: {$title}
Content:
{$truncatedBody}
Provide a JSON response with this exact structure:
{
"score": <number 1-100>,
"readability": "<brief assessment>",
"seo": "<brief assessment>",
"suggestions": [
"<specific improvement 1>",
"<specific improvement 2>",
"<specific improvement 3>"
]
}
Be constructive and specific. Return ONLY valid JSON.
PROMPT;
}
/**
* Parse the analysis response into structured data.
*/
protected function parseAnalysisResponse(string $response): array {
$data = json_decode($response, TRUE);
if (json_last_error() !== JSON_ERROR_NONE) {
return [
'score' => 0,
'suggestions' => ['Unable to analyze content. Please try again.'],
];
}
return $data;
}
}This service is doing the heavy lifting:
- Caching responses to avoid duplicate API calls
- Prompt engineering with clear, specific instructions
- Error handling with graceful degradation
- Token management by truncating content appropriately
Step 3: Create the Form Alterations
Now let’s add the AI buttons to the node edit form. Create ai_content_assistant.module:
<?php
/**
* @file
* AI Content Assistant module file.
*/
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\AjaxResponse;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\InvokeCommand;
use Drupal\Core\Ajax\MessageCommand;
/**
* Implements hook_form_BASE_FORM_ID_alter() for node_form.
*/
function ai_content_assistant_form_node_form_alter(&$form, FormStateInterface $form_state, $form_id) {
// Only add to article type (customize as needed)
$node = $form_state->getFormObject()->getEntity();
$enabledTypes = \Drupal::config('ai_content_assistant.settings')
->get('enabled_content_types') ?? ['article'];
if (!in_array($node->bundle(), $enabledTypes)) {
return;
}
// Add AI assistant fieldset
$form['ai_assistant'] = [
'#type' => 'details',
'#title' => t('🤖 AI Content Assistant'),
'#group' => 'advanced',
'#weight' => -100,
'#open' => TRUE,
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['ai-content-assistant-panel'],
],
];
// Meta description generator button
$form['ai_assistant']['generate_meta'] = [
'#type' => 'button',
'#value' => t('✨ Generate Meta Description'),
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => 'ai_content_assistant_generate_meta_callback',
'wrapper' => 'ai-meta-result',
'progress' => [
'type' => 'throbber',
'message' => t('AI is thinking...'),
],
],
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['ai-button', 'button--primary'],
],
];
$form['ai_assistant']['meta_result'] = [
'#type' => 'container',
'#attributes' => ['id' => 'ai-meta-result'],
];
// Tag suggestion button
$form['ai_assistant']['suggest_tags'] = [
'#type' => 'button',
'#value' => t('🏷️ Suggest Tags'),
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => 'ai_content_assistant_suggest_tags_callback',
'wrapper' => 'ai-tags-result',
'progress' => [
'type' => 'throbber',
'message' => t('Analyzing content...'),
],
],
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['ai-button'],
],
];
$form['ai_assistant']['tags_result'] = [
'#type' => 'container',
'#attributes' => ['id' => 'ai-tags-result'],
];
// Content analysis button
$form['ai_assistant']['analyze_content'] = [
'#type' => 'button',
'#value' => t('📊 Analyze Content Quality'),
'#ajax' => [
'callback' => 'ai_content_assistant_analyze_callback',
'wrapper' => 'ai-analysis-result',
'progress' => [
'type' => 'throbber',
'message' => t('Running AI analysis...'),
],
],
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['ai-button'],
],
];
$form['ai_assistant']['analysis_result'] = [
'#type' => 'container',
'#attributes' => ['id' => 'ai-analysis-result'],
];
// Attach library for styling
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'ai_content_assistant/ai_assistant';
}
/**
* AJAX callback to generate meta description.
*/
function ai_content_assistant_generate_meta_callback(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$response = new AjaxResponse();
try {
/** @var \Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service\AIService $aiService */
$aiService = \Drupal::service('ai_content_assistant.ai_service');
$title = $form_state->getValue('title')[0]['value'] ?? '';
$body = $form_state->getValue('body')[0]['value'] ?? '';
if (empty($body)) {
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('Please add some content before generating a meta description.'),
NULL,
['type' => 'warning']
));
return $response;
}
$metaDescription = $aiService->generateMetaDescription($title, $body);
// Update the meta description field if it exists
if (isset($form['field_meta_description'])) {
$response->addCommand(new InvokeCommand(
'[name="field_meta_description[0][value]"]',
'val',
[$metaDescription]
));
}
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('✅ Meta description generated! Review and adjust as needed.'),
NULL,
['type' => 'status']
));
}
catch (\Exception $e) {
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('AI service error: @message', ['@message' => $e->getMessage()]),
NULL,
['type' => 'error']
));
}
return $response;
}
/**
* AJAX callback to suggest tags.
*/
function ai_content_assistant_suggest_tags_callback(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$response = new AjaxResponse();
try {
/** @var \Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service\AIService $aiService */
$aiService = \Drupal::service('ai_content_assistant.ai_service');
$title = $form_state->getValue('title')[0]['value'] ?? '';
$body = $form_state->getValue('body')[0]['value'] ?? '';
$content = $title . ' ' . $body;
// Get existing tags from taxonomy
$existingTags = ai_content_assistant_get_existing_tags();
$suggestedTags = $aiService->suggestTags($content, $existingTags);
$tagList = implode(', ', $suggestedTags);
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('🏷️ Suggested tags: @tags', ['@tags' => $tagList]),
NULL,
['type' => 'status']
));
}
catch (\Exception $e) {
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('AI service error: @message', ['@message' => $e->getMessage()]),
NULL,
['type' => 'error']
));
}
return $response;
}
/**
* AJAX callback to analyze content.
*/
function ai_content_assistant_analyze_callback(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$response = new AjaxResponse();
try {
/** @var \Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Service\AIService $aiService */
$aiService = \Drupal::service('ai_content_assistant.ai_service');
$title = $form_state->getValue('title')[0]['value'] ?? '';
$body = $form_state->getValue('body')[0]['value'] ?? '';
$analysis = $aiService->analyzeContent($title, $body);
$message = t("📊 Content Score: @score/100\n\n@suggestions", [
'@score' => $analysis['score'] ?? 'N/A',
'@suggestions' => implode("\n• ", $analysis['suggestions'] ?? []),
]);
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
$message,
NULL,
['type' => 'status']
));
}
catch (\Exception $e) {
$response->addCommand(new MessageCommand(
t('AI service error: @message', ['@message' => $e->getMessage()]),
NULL,
['type' => 'error']
));
}
return $response;
}
/**
* Get existing taxonomy tags from the Tags vocabulary.
*/
function ai_content_assistant_get_existing_tags(): array {
$terms = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()
->getStorage('taxonomy_term')
->loadByProperties(['vid' => 'tags']);
$tagNames = [];
foreach ($terms as $term) {
$tagNames[] = $term->getName();
}
return $tagNames;
}Step 4: Add the Configuration Form
Editors need a way to configure their API key and settings. Create src/Form/SettingsForm.php:
<?php
namespace Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Form;
use Drupal\Core\Form\ConfigFormBase;
use Drupal\Core\Form\FormStateInterface;
/**
* Configuration form for AI Content Assistant.
*/
class SettingsForm extends ConfigFormBase {
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
protected function getEditableConfigNames() {
return ['ai_content_assistant.settings'];
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getFormId() {
return 'ai_content_assistant_settings';
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$config = $this->config('ai_content_assistant.settings');
$form['api_settings'] = [
'#type' => 'fieldset',
'#title' => $this->t('API Configuration'),
];
$form['api_settings']['openai_api_key'] = [
'#type' => 'password',
'#title' => $this->t('OpenAI API Key'),
'#description' => $this->t('Enter your OpenAI API key from platform.openai.com'),
'#default_value' => $config->get('openai_api_key'),
'#required' => TRUE,
];
$form['api_settings']['model'] = [
'#type' => 'select',
'#title' => $this->t('AI Model'),
'#options' => [
'gpt-4-turbo-preview' => 'GPT-4 Turbo (Recommended)',
'gpt-4' => 'GPT-4',
'gpt-3.5-turbo' => 'GPT-3.5 Turbo (Faster, cheaper)',
],
'#default_value' => $config->get('model') ?? 'gpt-4-turbo-preview',
];
$form['content_types'] = [
'#type' => 'fieldset',
'#title' => $this->t('Content Type Settings'),
];
$contentTypes = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()
->getStorage('node_type')
->loadMultiple();
$options = [];
foreach ($contentTypes as $type) {
$options[$type->id()] = $type->label();
}
$form['content_types']['enabled_content_types'] = [
'#type' => 'checkboxes',
'#title' => $this->t('Enable AI Assistant for'),
'#options' => $options,
'#default_value' => $config->get('enabled_content_types') ?? ['article'],
];
return parent::buildForm($form, $form_state);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function submitForm(array &$form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$this->config('ai_content_assistant.settings')
->set('openai_api_key', $form_state->getValue('openai_api_key'))
->set('model', $form_state->getValue('model'))
->set('enabled_content_types', array_filter($form_state->getValue('enabled_content_types')))
->save();
parent::submitForm($form, $form_state);
}
}Add the routing:
# ai_content_assistant.routing.yml
ai_content_assistant.settings:
path: '/admin/config/content/ai-assistant'
defaults:
_form: '\Drupal\ai_content_assistant\Form\SettingsForm'
_title: 'AI Content Assistant Settings'
requirements:
_permission: 'administer ai content assistant'And permissions:
# ai_content_assistant.permissions.yml
administer ai content assistant:
title: 'Administer AI Content Assistant'
description: 'Configure API keys and settings for the AI assistant.'
use ai content assistant:
title: 'Use AI Content Assistant'
description: 'Access AI-powered content suggestions while editing.'Step 5: Add Some Polish with CSS
Let’s make our AI panel look premium. Create css/ai_assistant.css:
/* AI Content Assistant Styles */
.ai-content-assistant-panel {
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #1a1f35 0%, #0d1117 100%);
border: 1px solid #00F0FF33;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 1.5rem;
}
.ai-content-assistant-panel summary {
color: #00F0FF;
font-weight: 600;
font-size: 1.1rem;
}
.ai-button {
margin: 0.5rem 0.5rem 0.5rem 0;
padding: 0.75rem 1.5rem;
background: transparent;
border: 1px solid #00F0FF;
color: #00F0FF;
border-radius: 8px;
cursor: pointer;
font-weight: 500;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
.ai-button:hover {
background: #00F0FF20;
box-shadow: 0 0 20px #00F0FF40;
transform: translateY(-2px);
}
.ai-button.button--primary {
background: #00F0FF;
color: #0d1117;
}
.ai-button.button--primary:hover {
background: #33F3FF;
box-shadow: 0 0 30px #00F0FF60;
}
/* Loading state */
.ajax-progress-throbber {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 0.5rem;
color: #00F0FF;
font-size: 0.9rem;
}Create the library file:
# ai_content_assistant.libraries.yml
ai_assistant:
css:
theme:
css/ai_assistant.css: {}Testing Your AI Assistant
Enable the module and try it out:
drush en ai_content_assistant -y
drush crNow navigate to /admin/config/content/ai-assistant and add your OpenAI API key. Then create or edit an article—you’ll see the AI Content Assistant panel in the sidebar!
| Feature | What to Test |
|---|---|
| Meta Description | Add body content, click generate, verify output |
| Tag Suggestions | Write an article, click suggest, check relevance |
| Content Analysis | Complete article, run analysis, review score |
Production Considerations
Before deploying to production, consider these optimizations:
1. Rate Limiting
Add rate limiting to prevent API abuse:
/**
* Check rate limit before API call.
*/
protected function checkRateLimit(): bool {
$cache = \Drupal::cache();
$userId = \Drupal::currentUser()->id();
$cacheId = "ai_rate_limit:{$userId}";
$current = $cache->get($cacheId);
$count = $current ? $current->data : 0;
if ($count >= 50) { // 50 requests per hour
return FALSE;
}
$cache->set($cacheId, $count + 1, time() + 3600);
return TRUE;
}2. Cost Monitoring
Track API usage for budget management:
| Model | Input Cost | Output Cost | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4 Turbo | $0.01/1K | $0.03/1K | Production |
| GPT-3.5 Turbo | $0.0005/1K | $0.0015/1K | Development |
3. Fallback Handling
Always have graceful degradation:
if (!$this->isAIServiceAvailable()) {
return $this->getFallbackResponse($feature);
}What’s Next?
You now have a fully functional AI Content Assistant in Drupal 11.3. But this is just the beginning. Here are some advanced features to consider:
🚀 Level Up Ideas:
- Content translation - Auto-translate to multiple languages
- Image alt-text generation - AI describes uploaded images
- Tone adjustment - Professional ↔ Casual content conversion
- Plagiarism detection - Check content originality
- Competitor analysis - Compare with top-ranking content
Conclusion: The Future is AI-Augmented
We’ve built something powerful today. Not AI that replaces your editors, but AI that amplifies them. AI that handles the tedious parts so your team can focus on what matters: creating content that connects with humans.
Drupal 11.3 is uniquely positioned for this future. Its robust API architecture, flexible plugin system, and enterprise-grade foundation make it the perfect canvas for AI innovation.
The question isn’t whether your CMS should integrate AI—it’s whether you’ll be the one leading that transformation.
Now go build something legendary.
Found this helpful? Share it with your team. Have questions or improvements? Connect with me on LinkedIn or check out my other Drupal deep-dives.
